Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals within a joint. It most commonly affects the big toe, although other joints in the foot and ankle can be involved. One of the key signs of gout is sudden, intense pain that often begins at night. The joint may become red, swollen, warm, and extremely tender to the touch. Even the pressure of a bedsheet can feel unbearable. The skin over the area may appear tight or shiny, and walking can become very difficult. Gout attacks can last several days and may return if the underlying uric acid levels are not controlled. Risk factors include diet, dehydration, certain medications, and family history. A podiatrist can evaluate the painful joint, review medical history, and coordinate testing to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and preventing future attacks. If you have signs of gout, it is suggested that you make an appointment with a podiatrist for proper evaluation and care.
Gout is a foot condition that requires certain treatment and care. If you are seeking treatment, contact Richard DiBacco, DPM from Podiatry Associates of Erie, Inc.. Our doctor will treat your foot and ankle needs.
What Is Gout?
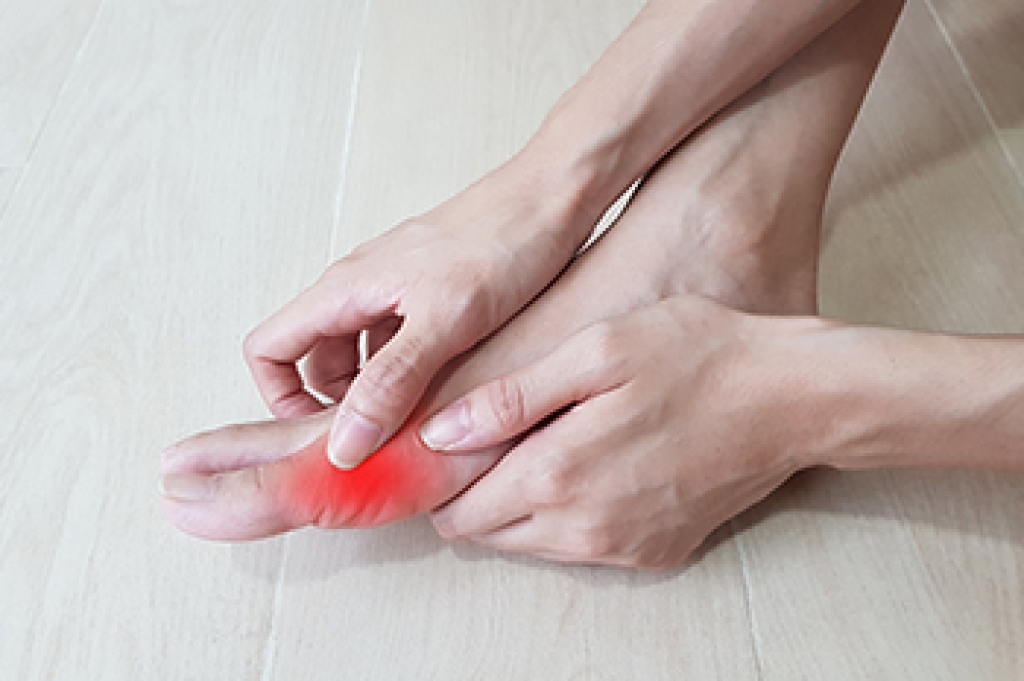
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream. It often develops in the foot, especially the big toe area, although it can manifest in other parts of the body as well. Gout can make walking and standing very painful and is especially common in diabetics and the obese.
People typically get gout because of a poor diet. Genetic predisposition is also a factor. The children of parents who have had gout frequently have a chance of developing it themselves.
Gout can easily be identified by redness and inflammation of the big toe and the surrounding areas of the foot. Other symptoms include extreme fatigue, joint pain, and running high fevers. Sometimes corticosteroid drugs can be prescribed to treat gout, but the best way to combat this disease is to get more exercise and eat a better diet.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact one of our offices located in Erie and Meadville, PA, . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.